GRID LIVING: 3 HONG KONG HOMES. |
||
Hong Kong flats are notoriously tiny. When furnishing one, a minimalist approach may seem appropriate. A few select pieces of designer furniture, some stylish armoires to hide the clutter and voilà: it almost looks like a viable space for living in.
Yet TypicalPlan believes this is a self-defeating strategy. Inevitably, it is only a matter of time before the onslaught of consumerist materialism destabilises the carefully curated harmony, and clutter insidiously impinges on the interiors. This is especially true for a cramped apartment with limited storage space.
Besides, even just a few pieces of normal-sized designer furnishings can create a comically unbalanced interior in these absurdly scaled-down living spaces. One is reminded of the giant rock occupying a room in Magritte’s painting “L’anniversaire”.
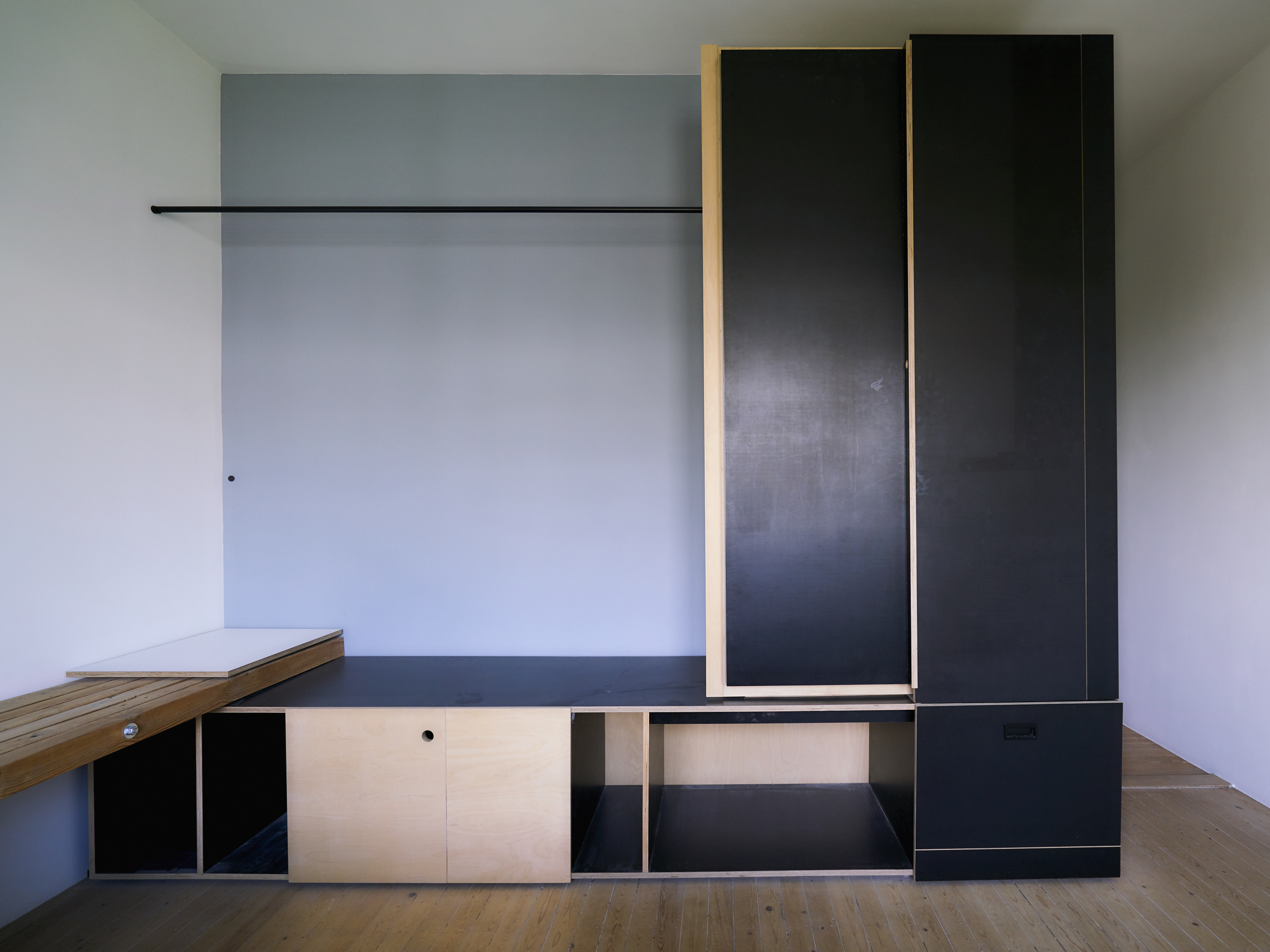
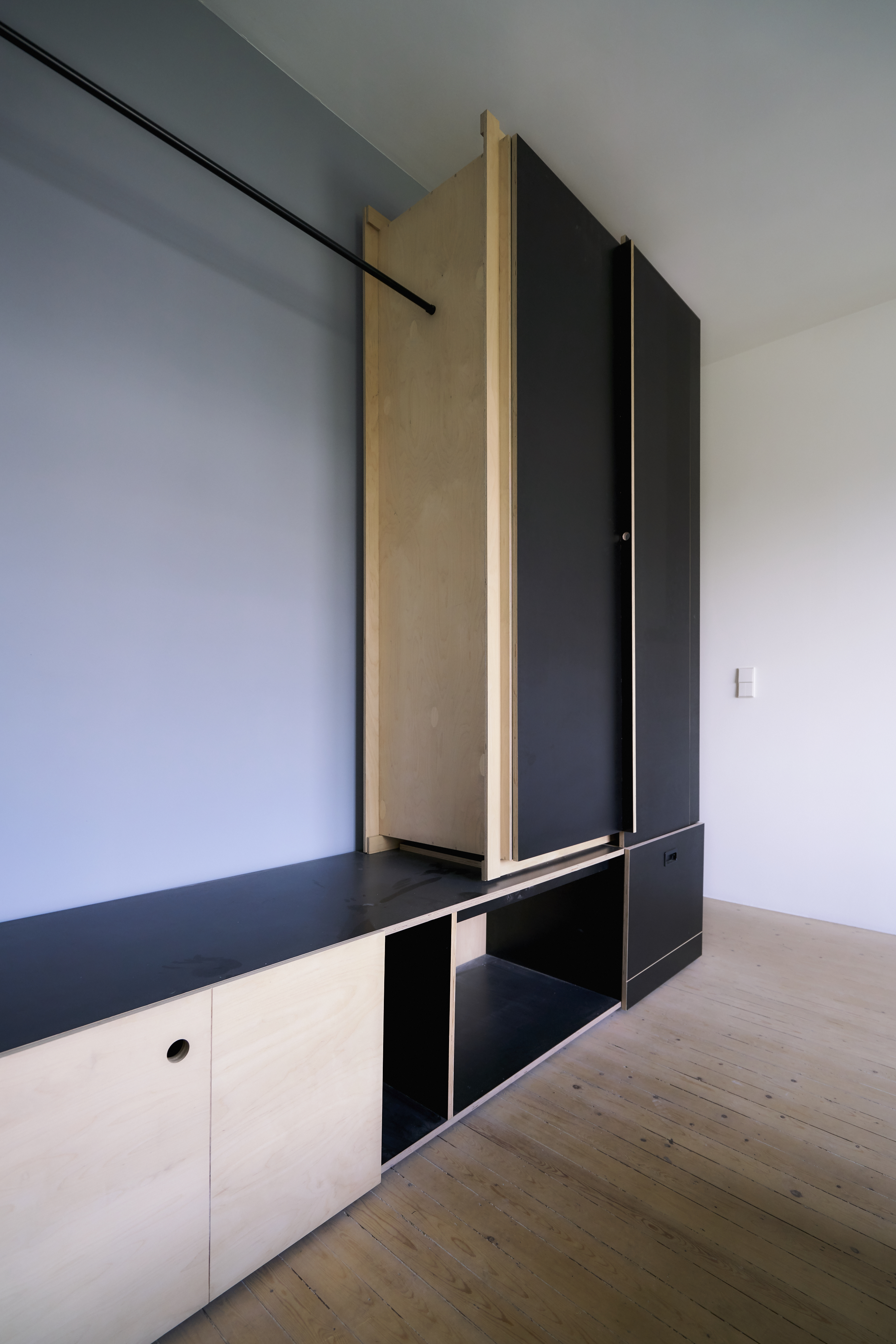
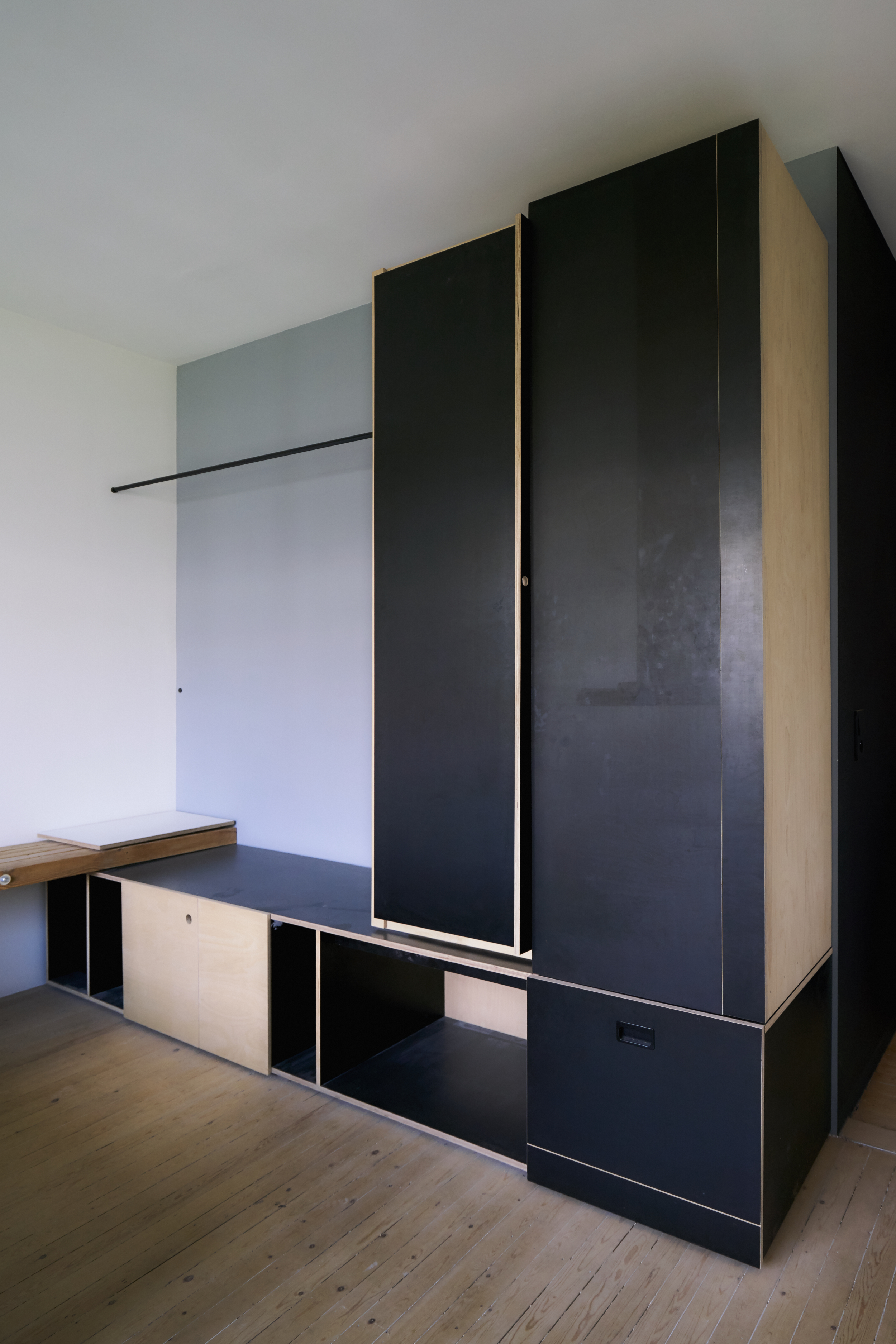
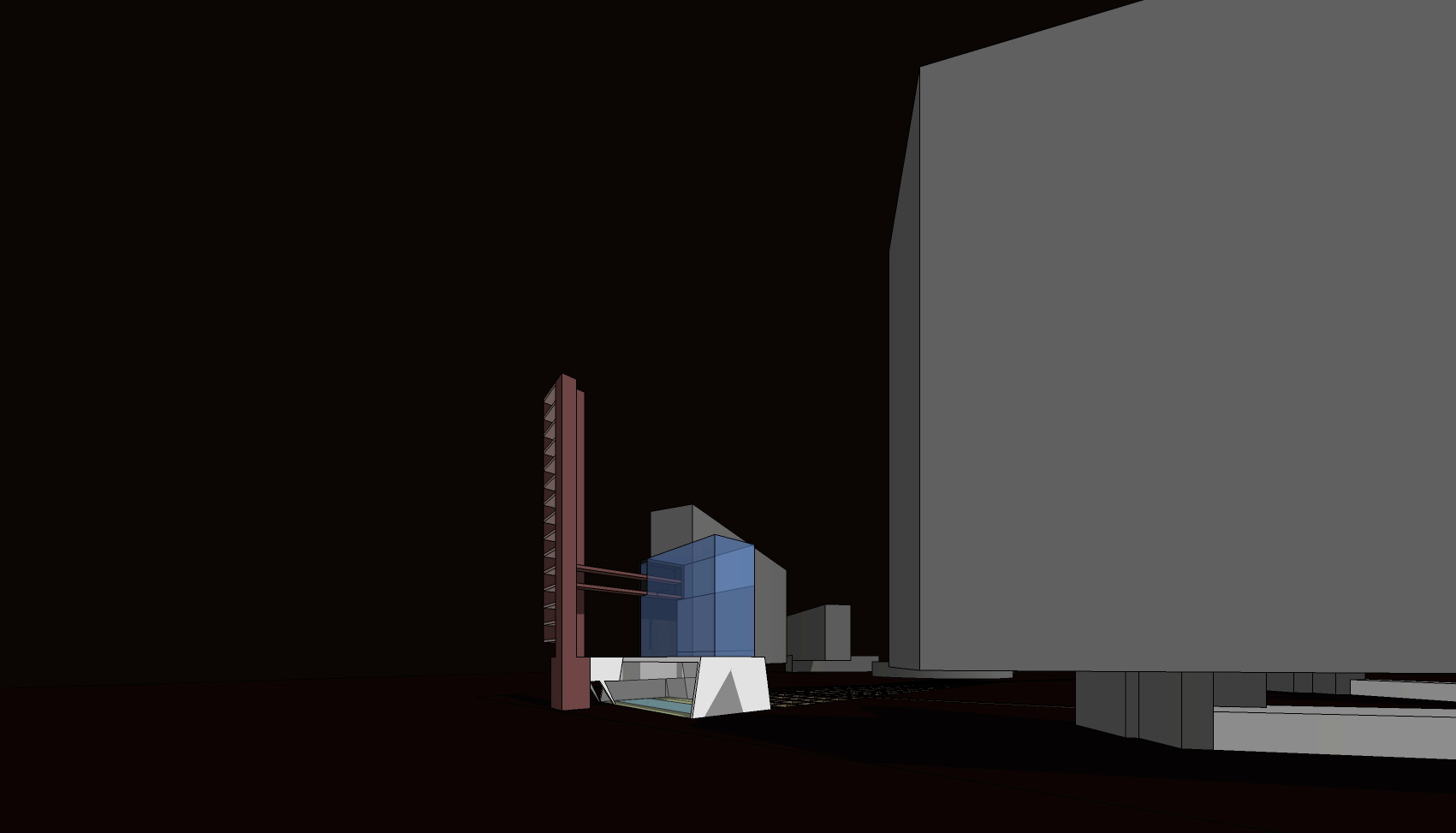
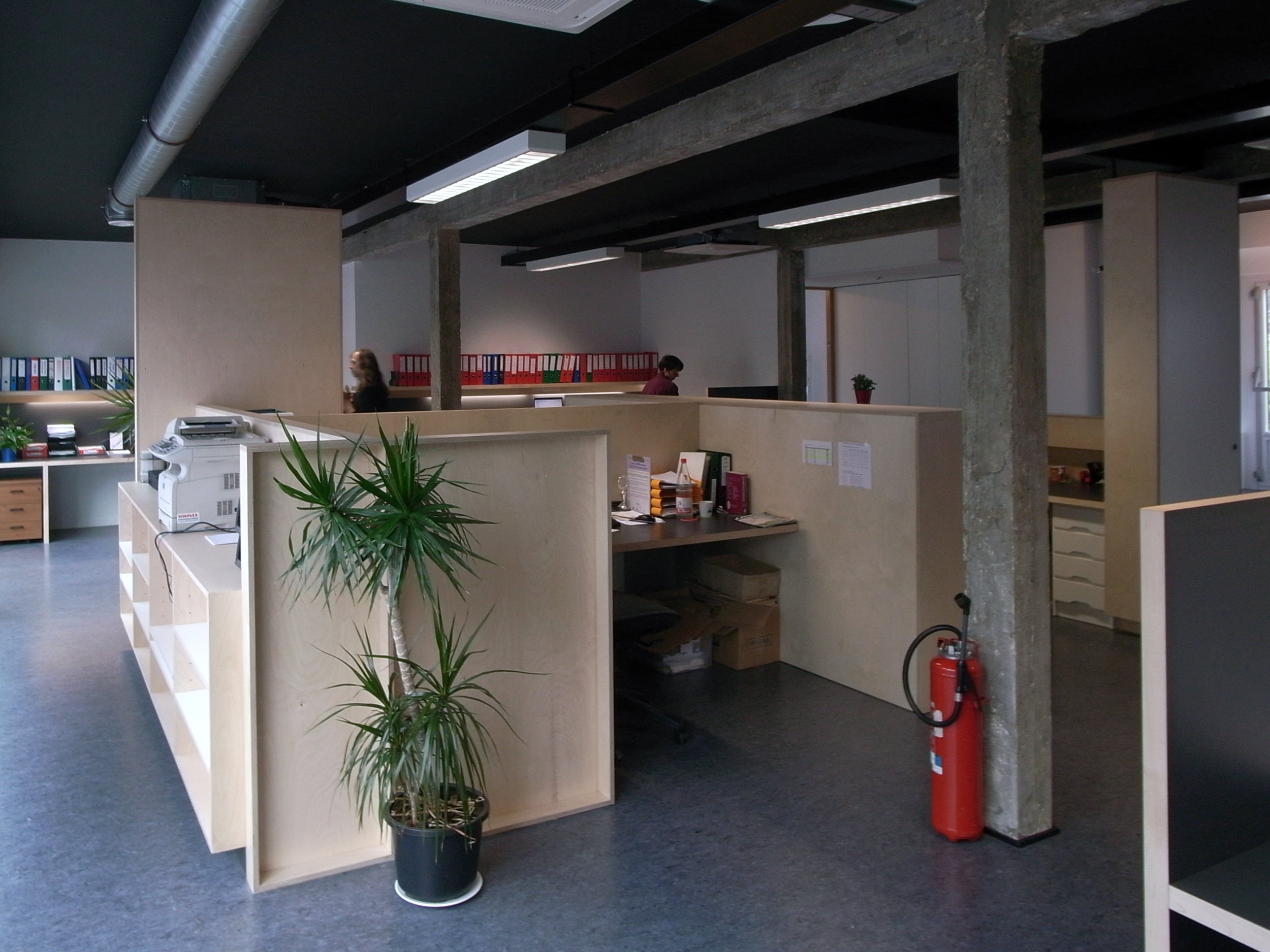
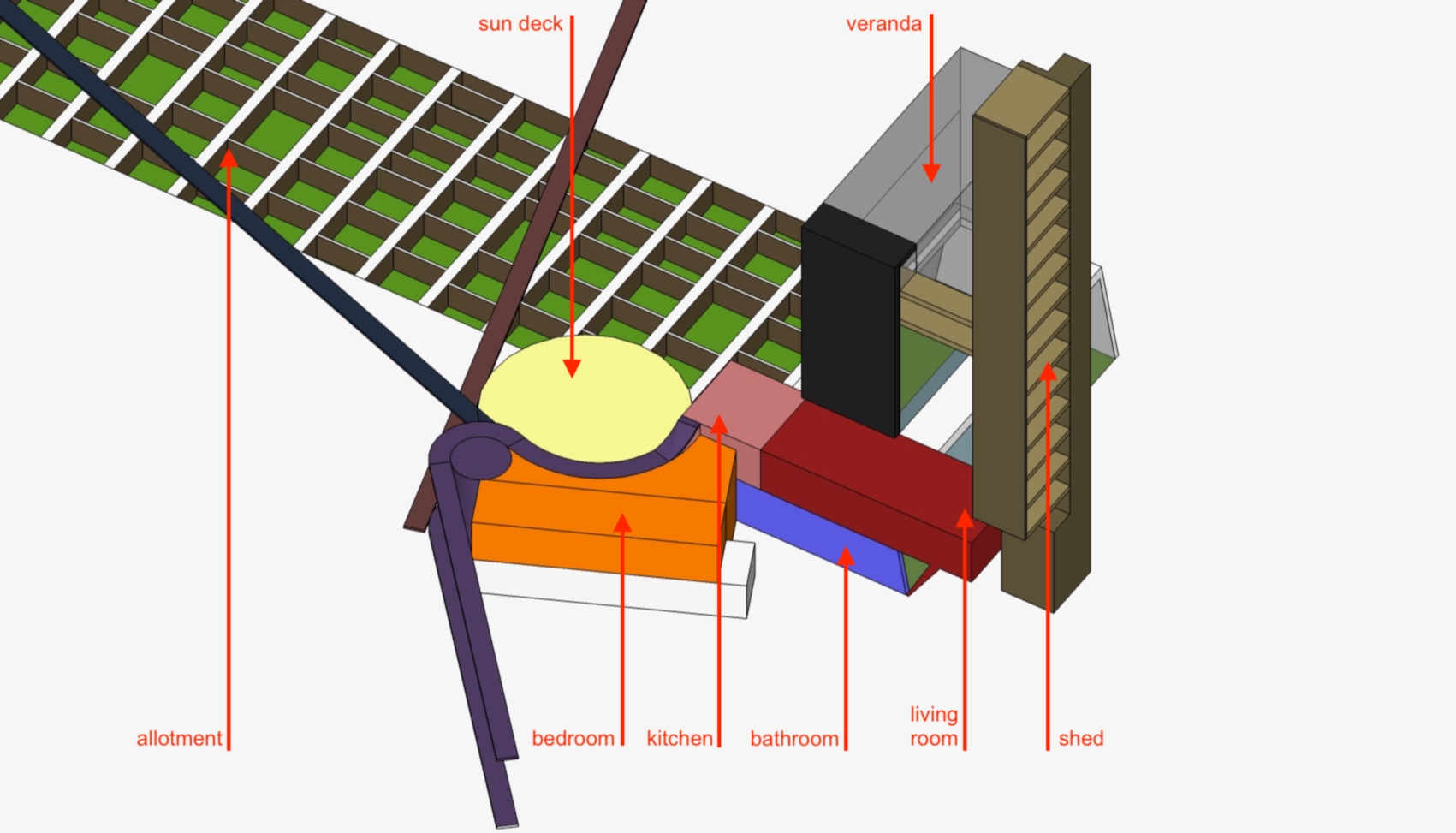
For three apartments inhabited over a 12-year period, a radically different approach was adopted. Instead of a minimal, object-centred intervention, the rooms are fitted out with a space-filling framework. This structure, composed out of a proprietary wire-shelving system, occupies, organises and unifies the interior. Instead of tables, chairs and sofas squatly dominating space, an expansive grid of shelving lines the walls, smoothly integrating different functions: storage, sleeping, eating, working, relaxing…
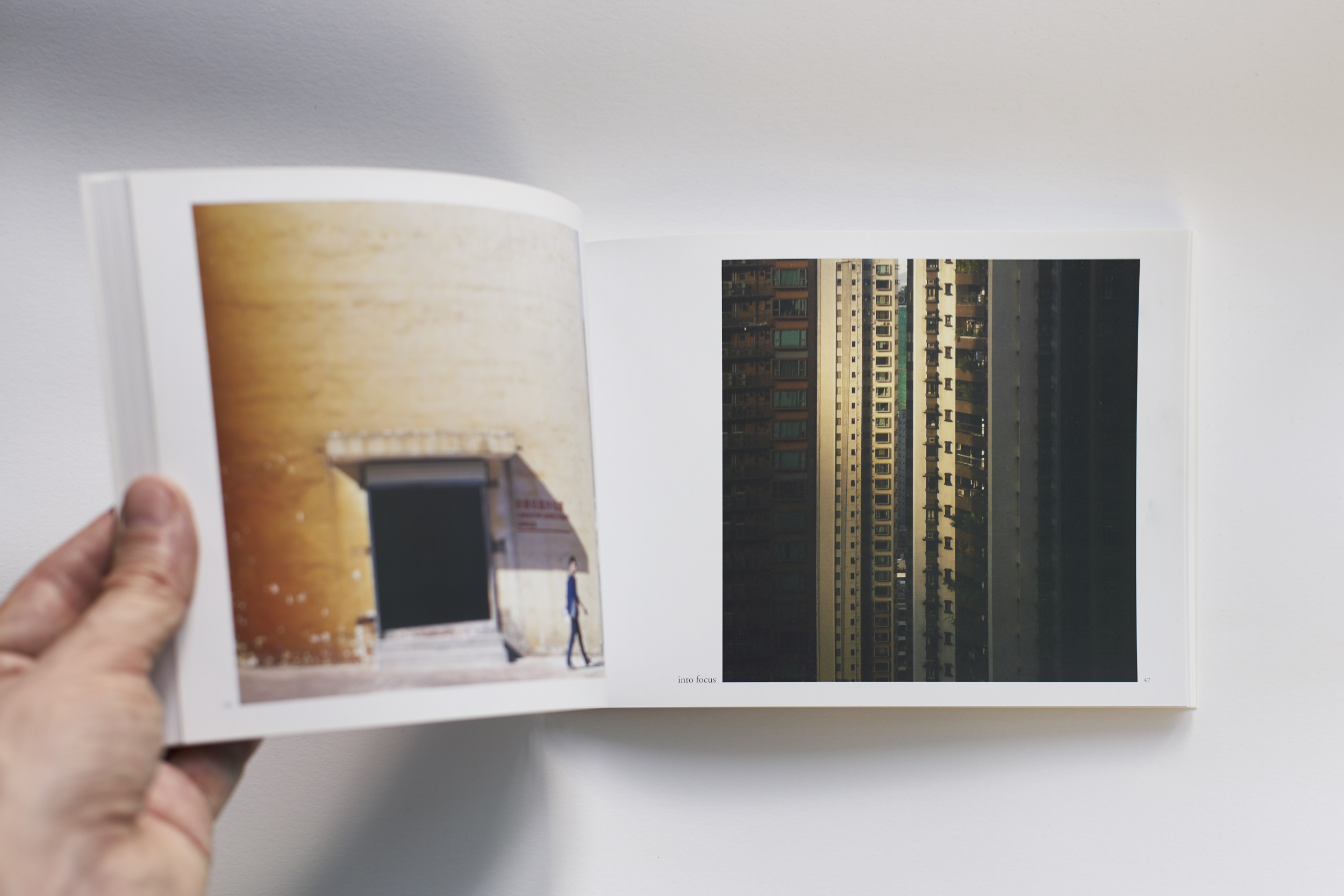
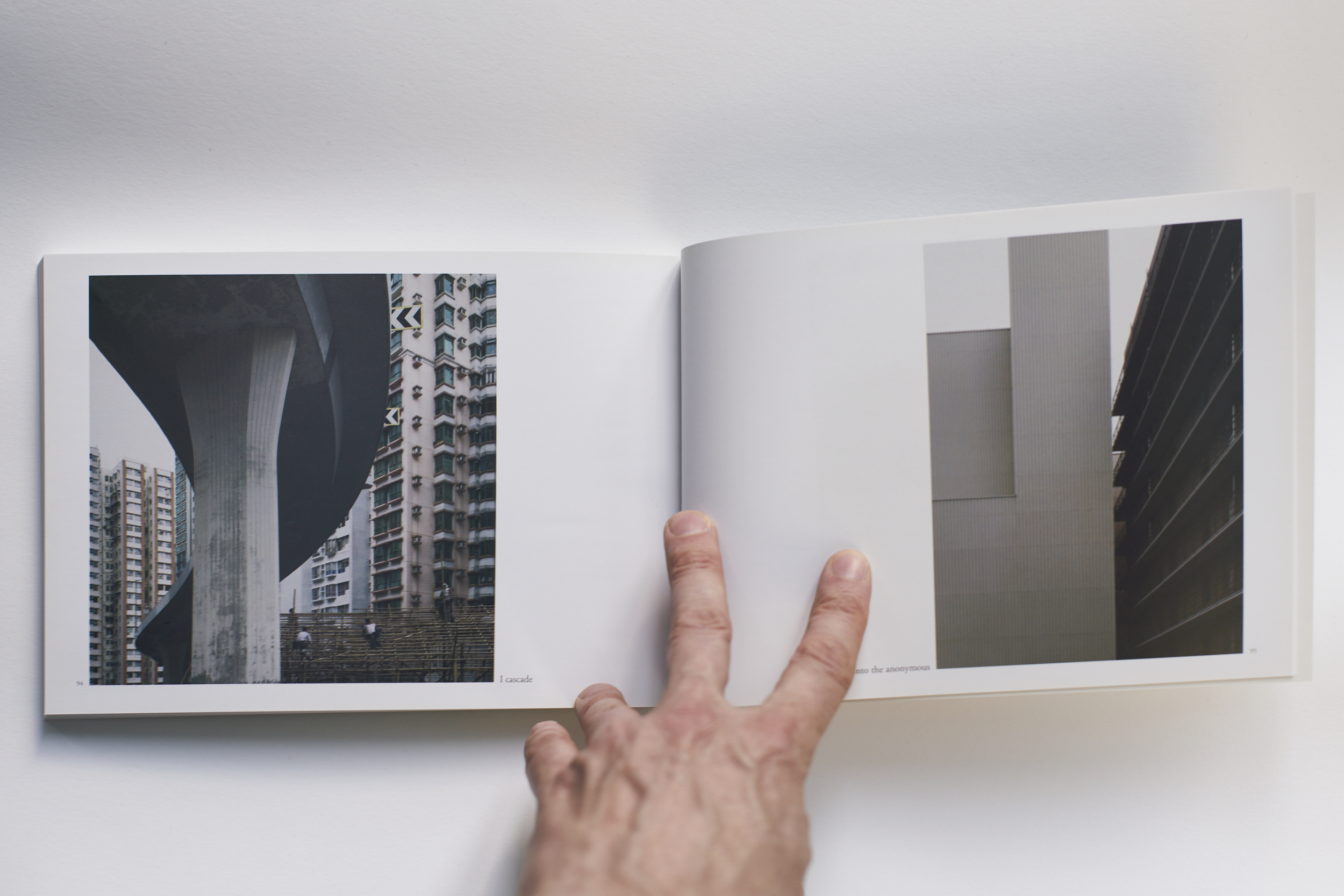
This approach draws inspiration from Hong Kong’s urban environment. The shelving system reminds us of both bamboo scaffolding and the irregular skyline. Functionally it offers an indoor continuation of the juxtapositions found on the streets outside: the coffee machine is standing just two shelves above the shoes cabinet, your drawing supplies are stored next to where you eat your soup. The vibrant chaos of Hong Kong is not denied but celebrated in this interior, translated into the miscellanea of daily life being displayed on the wire shelves or inside translucent storage boxes.
“One is reminded of Toetanchamon in his tomb, surrounded by his earthly possessions, everything within reach.
(Is this the afterlife? Maybe it was, for just a while; but everything must come to an end, also this mummified lifestyle…)”
Like the incongruities of the Hong Kong streetscape, this design cannot be reduced to one item or object or quality, but creates an immersive environment which should be considered in its totality. This interior is anti-aesthetic, ephemeral and changeable. It largely ignores the typical preoccupations of interior design (materiality, texture, surface, form); instead it speaks the language of urbanism: zoning, layering, programming. It reinforces the continuity of space rather than fragmenting it through the introduction of an object/background duality. It does not hide the clutter, but uses it to its advantage. In a way, the clutter IS the interior design…
location: Hong Kong
year: 2014–2025
project: interior design for three apartments in Hong Kong (Spring Garden / Mercury / Electric)
architect: Hans Leo Maes / TypicalPlan